1. Interrupt
Interrupt
1. Preview
1) Why Interrupt?
Operating System은 결국 Service routine들의 모음이라고 할 수 있고, 이 Service routine들은 Interrupt라고 불리는 상황에서부터 실행된다.
CPU는 이 Service routine들을 반복적으로 수행하게 되는데, 이때 중간중간 입출력 장치같은 외부 장치나 Application으로부터 Call이 발생하여 특정 Service routine을 우선적으로 수행해야 하는 경우가 생긴다. 따라서 이런 Call(Interrupt)들을 효율적으로 관리할 수 있도록 하는 작업이 필요하다.
즉, Interrupt가 존재함으로써 CPU는 프로그램을 실행하면서, 하던 일을 멈추고, 내/외부 입력 사항에 대한 처리를 할 수 있게 된다.
2) 종류
Interrupt들은 크게 다음 3가지의 경우에 발생된다.
- System Call Interrupt
- application의 요청
- Exception Interrupt
- Error (ex.Zero Division Error)
- Hardware Interrupt
- External Hardware Event (ex.Keyboard Input)
3) 참고
가끔 assembly어가 사용되어 간단한 설명이 필요할 것 같다.
MOV a, b # b값을 a레지스터에 저장 PUSH a # a에 저장되어 있는 데이터를 stack으로 옮긴다. # ESP레지스터의 값은 -4 POP a # stack에 저장되어 있는 값을 a로 옮긴다 # ESP레지스터의 값은 +4 INT a # a번 interrupt를 발생시킴
2. Interrupt Handling Process
1) Interrupt 발생
SoftWare Interrupt
Hardware Interrupt
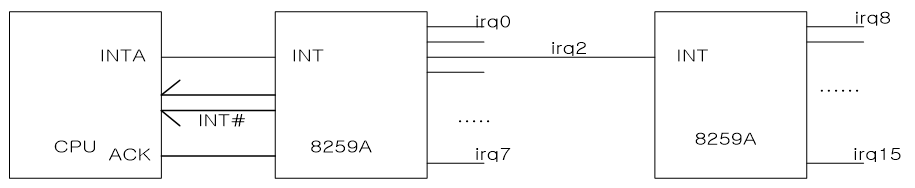
Hardware Interrupt는 CPU옆의 IRQ(Interrupt Request) Line을 통해 8259A Interrupt Controller에 저장됨
(모든 Hardware Devices는 8259A에 연결되어 있음)8259A장치는 CPU에 Interrupt가 발생했다는 신호를 보냄
(이때Interrupt Number = IRQ line Number + 32)(참고)
Timer: IRQ0 line 사용
Keyboard: IRQ1 line 사용
2) Interrupt 감지
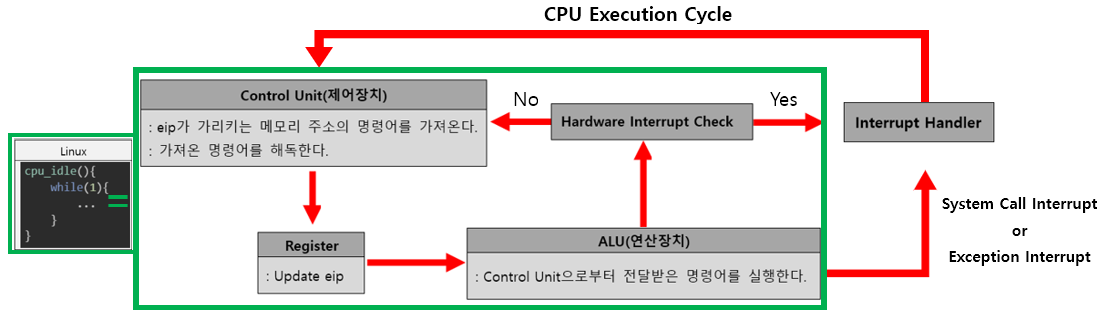
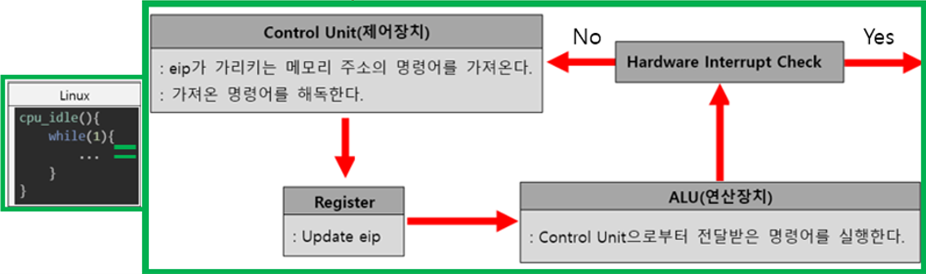
CPU Cycle
- Software Interrupt
- 전달받은 명령 수행 도중 Error발생(Exception Interrupt)
- 전달받은 명령이 System Call명령임(System call Interrupt)
- Hardware Interrupt
- CPU는 하나의 명령어를 실행할 때마다 IRQ Line을 확인
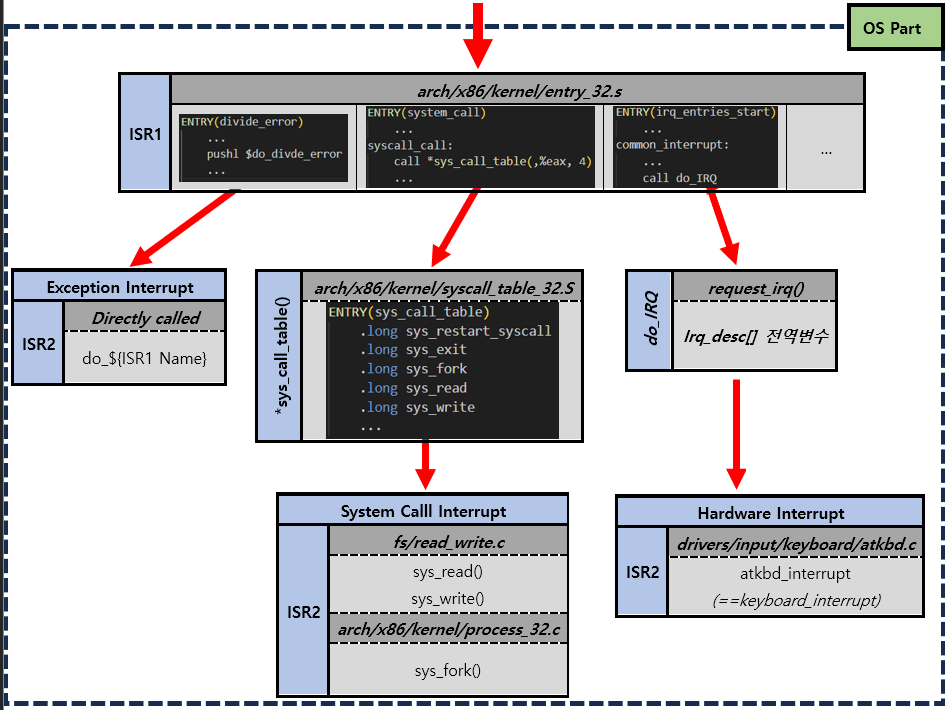
3) ISR(Interrupt Service Routine)
특정 Interrupt에 대한 수행 지침
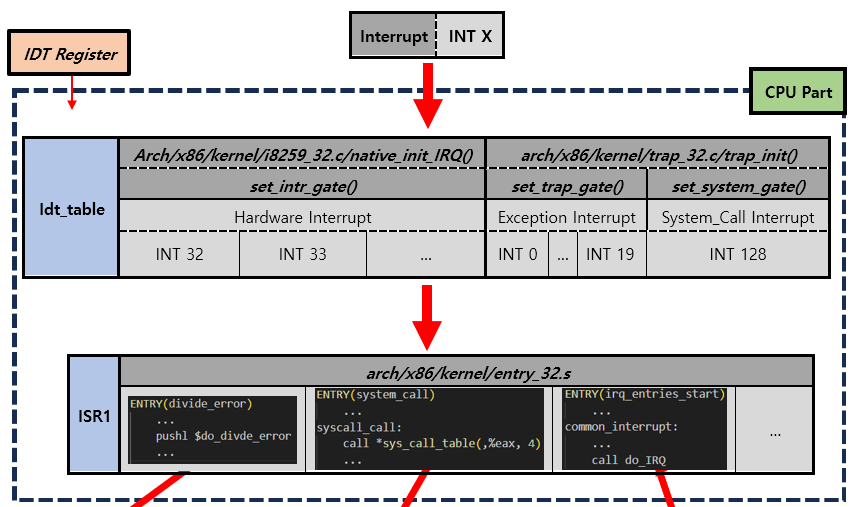
CPU Part
현재 상태(
cs,eip register,eflag)를 PCB(Process Control Block)에 저장IDTR Register를 통해 IDT(Interrupt Description Table)의 주소를 가져옴
IDT[x]가 가리키는 주소로 jump하여 해당 주소에 있는 Program (==ISR1) 을 실행
(IDT의 각 entry는 8byte이다.)
(ISR1은arch/x86/kernel/entry_32.S에 정의되어 있다.)참고
Interrupt Vector Table = IDT(Interrupt Description Table)OS Part (==ISR1 Part)
나머지 Register의 현재상태를 저장
Actual Interrupt Handler(==ISR2) Process를 실행
(ISR2는Various place에 정의되어 있다.)
(system call의 경우arch/x86/kernel/syscall_table_32.S에 정의되어 있다.)
- Recover
- PCB로 대피시킨 Register복원
- ISR실행 전의 코드로 복귀
- *(참고)
do_divide_error은 ISR2 코드가 실물로 존재하지 않고 Compile Time에 생성된다.- Hardware Interrupt 참고할 만한 블로그*
Set ISR1
- Hardware Interrupt
(위치):arch/x86/kernel/i8259_32.c/native_init_IRQ()
- Software Interrupt
(위치):arch/x86/kernel/traps_32.c/trap_init()```cpp void __init trap_init(void){ int i; #ifdef CONFIG_EISA void __iomem *p = early_ioremap(0x0fffd9, 4); if(read1(p)==’E’ + (‘I’«8) + (‘S’«16>) + (‘A’«24)) EISA_bus = 1; early_iounmap(p, 4);
#endif#ifdef CONFIG_X86_LOCAL_APIC init_apic_mappings(); #endif
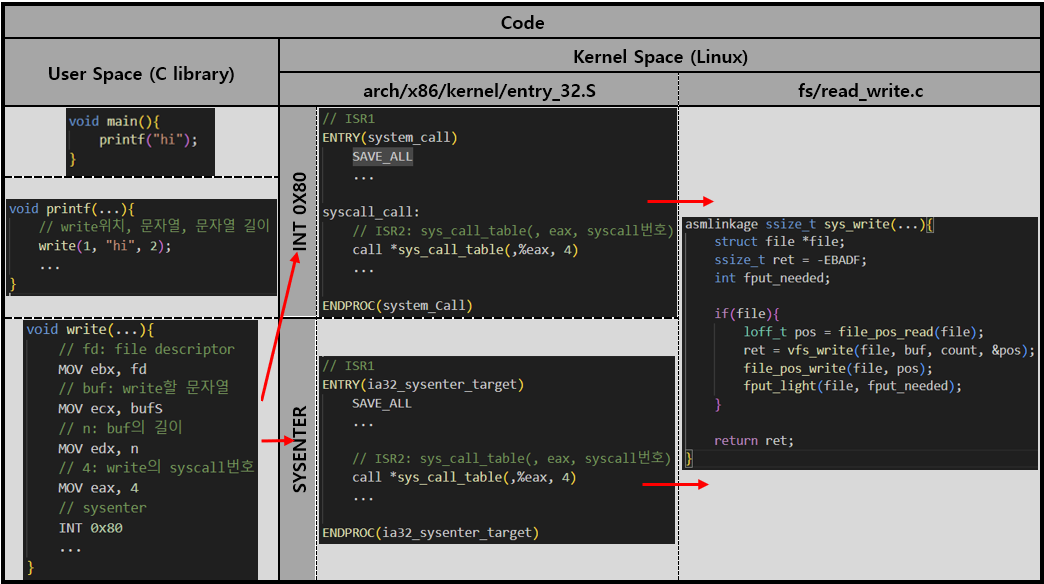
3. System Call Interrupt
1) System Call 동작과정
동작 과정
System Call은 모두 128의 Interrupt Number를 갖는다.
따라서 각 System call Number가 따로 존재하여 System Call Interrupt의 동작 과정을 구분짓고, 이 동작 과정은 다음과 같다.
MOV eax, syscall# # sys_call번호를 eax레지스터에 저장 INT 0X80 # 128번 Interrupt를 발생시킴즉, 어떤 System Call을 호출해야하는 함수를 작성하면
- 128번 Interrupt를 호출하는 Assembly어로 변경
arch/x86/kernel/entry_32.S에서 ISR1 호출fs/read_write.c에서 ISR2 호출과 같은 순서를 통해 동작한다.
(참고):
C에서는syscall(x)함수를 통해 syscall을 바로 사용할 수 있다.
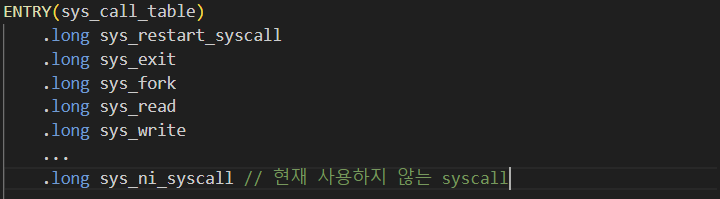
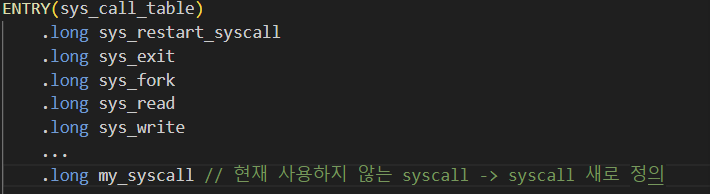
2) System Call 등록
등록 방법
sys_ni_syscall
arch/x86/kernel/syscall_table_32.S에 보면sys_ni_syscall이라는 system_call이 여러개가 눈에 띈다.해당 시스템 콜은
kernel/sys_ni.c에 정의되어 있다.확인해 보면
-ENOSYS를 바로 return 하고있는 것을 볼 수 있는데, 이것은 아직 구현되지 않은 함수를 사용할 때 반환되는 오류코드이다.