4. File System(memory)
앞서 우리는 On-Disk File System에 대해서 알아보았다.
이 On-Disk File System은 Inode를 통해 Time Efficiency를 효과적으로 늘렸지만 다음과 같은 단점이 여전히 존재했다.
- 여전히 느리다.
- 여러 Disk의 관리가 힘들다.
(System이 여러개의 Disk를 가지면 각 Disk마다 File System이 있어야 함)
따라서 On-Memory File System(Virtual File System)이라는 방법을 통해 위의 두 문제를 해결했는데, 주된 Concept은 다음과 같다.
- 속도향상 → **Caching**
- 자주 접근하는 Block은 System Memory에 복사해 놓고 사용
- 속도향상 → **Caching**
- 여러 Disk 관리 → **Mounting**
- File System에 File System을 연결하여 하나의 File System을 통해 여러개의 File System을 관리하는 방법
- 여러 Disk 관리 → **Mounting**
On-Memory File System
Caching
Caching은 자주 접근하는 정보를 미리 System Memory에 저장해 놓고 필요할때마다 사용하는 것으로, Disk에 매번 접근할 필요가 없기 때문에 속도향상에 매우 큰 영향을 준다.
이때 Cache의 대상이 되는 것은 다음과 같다.
- Super Block
- Group Descriptor
- DBM(Data Block Bitmap)
- IBM(Inode Bitmap)
이때, System Memory는 해당 Block이 어느 Disk의 Block인지에 대한 정보 등을 같이 알고 있어야 하기 때문에 원래 데이터에 Additional Data를 추가하고,
이렇게 Cache된 Data를 Linked List에 연결하여 보관한다.
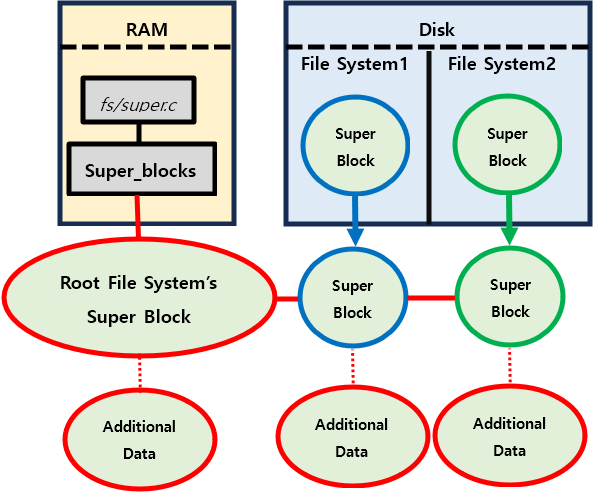
1) Super Block
Define
On-Memory Super Block은 Mount된 On-Disk File System에서 다음의 정보를 결합하여 새로운 super block을 만든다.
(include/linux/fs.h에 정의되어 있다.)
ext2_super_blockAdditional info이때 이 super block은
fs/super.c에 선언된super_blocks라는 linked list에 연결되어 cache된다.Example
Cache된 모든 Super Block을 출력하기
list_for_each_entry([정보를 담을 변수, linked list, next pointer])MAJOR(): Device 번호MINOR(): 그 Device의 종류안에서 구별할 수 있는 번호
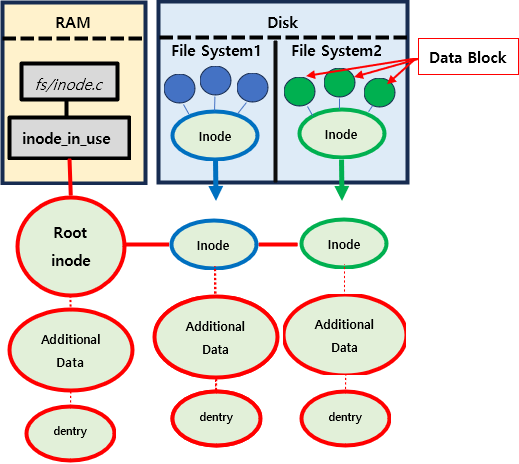
2) Inode
Define
On-Memory Inode는 Mount된 On-Disk File System에서 Inode의 정보와 다음의 정보를 결합하여 새로운 super block을 만든다.
(include/linux/fs.h에 정의되어 있다.)
ext2_inodeAdditional infodentry이때 inode는
fs/inode.c에 선언된inode_in_use라는 linked list에 연결되어 cache된다.(dentry: Directory Entry의 약자로, inode를 효율적으로 관리하기 위한 자료구조)
Example
Cache된 모든 Inode 출력하기
3) 그 밖의 Block들
위의 두 자료구조 외에도 자주 사용하는 정보(Block)들도 Block단위로 따로 Cache해둔다.
이때 사용하는 구조체는 다음과 같다.
이때 이 Block들은 최대한 빨리 접근하는 것이 중요하기 때문에,
linked list가 아닌 **hash table**을 사용해서 Cache한다.(linux 2.6이상부터는 hash table도 아닌 더 복잡한 자료구조를 사용해 Cache한다.)
Mounting
1) Concept
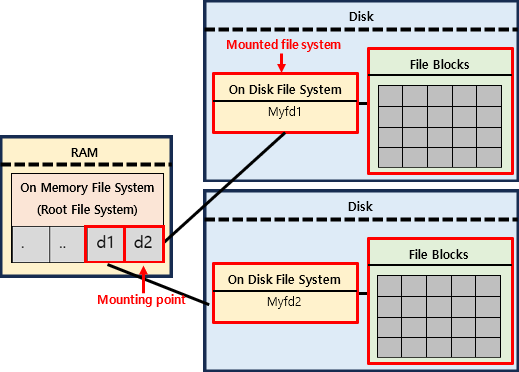
Root File System
System Memory에 가장 처음 Cache되는 File System으로 다른 On Disk File System이 여기에 mount된다.
mounted file system
mounting point
2) 과정
1. Cache the Mounted File System
Mounted File System을 Cache하여 System Memory로 가지고 온다.
이때, Cache하는 정보는 다음 두가지이다.
- superblock
- root inode
(Mounted File System의 inode 중 root inode만을 Cache한다.)2. Cache the Mounting Point’s Inode
다음으로는 Mounted File System을 연결할 Mounting Point를 가져와야 한다.
이를 위해서 Mounting Point의 Inode를 Cache한다.(즉,
'/'(root)부터 Mounting Point까지 경로상의 모든 dir에 대한 inode를 Cache해야 한다.)3. Mounted File System을 Mounting Point에 연결
연결 과정은 다음과 같다.
a) Mounting Point가 되는 File의 Inode를 찾아 그 dentry의 d_mounted += 1
b)
vfsmount{}자료구조를 통해 연결정보를 저장
- mnt_mountpoint
- mounting point위치 저장
- mnt_root
- Mounted File System의 root inode 저장
- mnt_sb
- Mounted File System의 super block 저장
c)
vfsmount{}자료구조를 mount_hastable에 저장
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)